Version History automatically tracks every significant change to your pipeline, creating restore points that protect your work and enable complete visibility into how your pipelines evolve.
Feature Benefits
Restore Pipelines: Review past versions of a data pipeline and restore a previous version into production.
Save Checkpoints: Create intentional save points at key pipeline building milestones for future reference.
Review and Audit: Data Architects can review changes made by Data Engineers, seeing exactly what was added, removed, or updated.
How Versions Are Created
Automatic Saves
The system automatically saves your work whenever you make a change.
Auto-save does not trigger if no modifications occur.
Prevents duplicate versions: if no change is detected, the system will not create a new version.
Major Actions
Deployments, reverts, and template changes automatically generate new versions.
Guarantees milestone states are always recorded.
Manual Saves
Use the Save New Version button to capture a checkpoint.
Add a description (e.g., “Added downtime model”) for clarity.
Best practice: keep descriptions short, clear, and milestone-focused for instant recall.
How Versions Are Organized
Grouped by day, with the newest at the top.
Each version includes:
Type (auto-save, manual, deployment, revert, template change)
User who created it
Timestamp
Title/description (if manually saved)
No version limit. Only new or changed work is saved, ensuring history remains clean.
How to Use Version History
1. Open Version History
Open a pipeline in Pipeline Builder.
Click the Version History button.
Select a version to load.
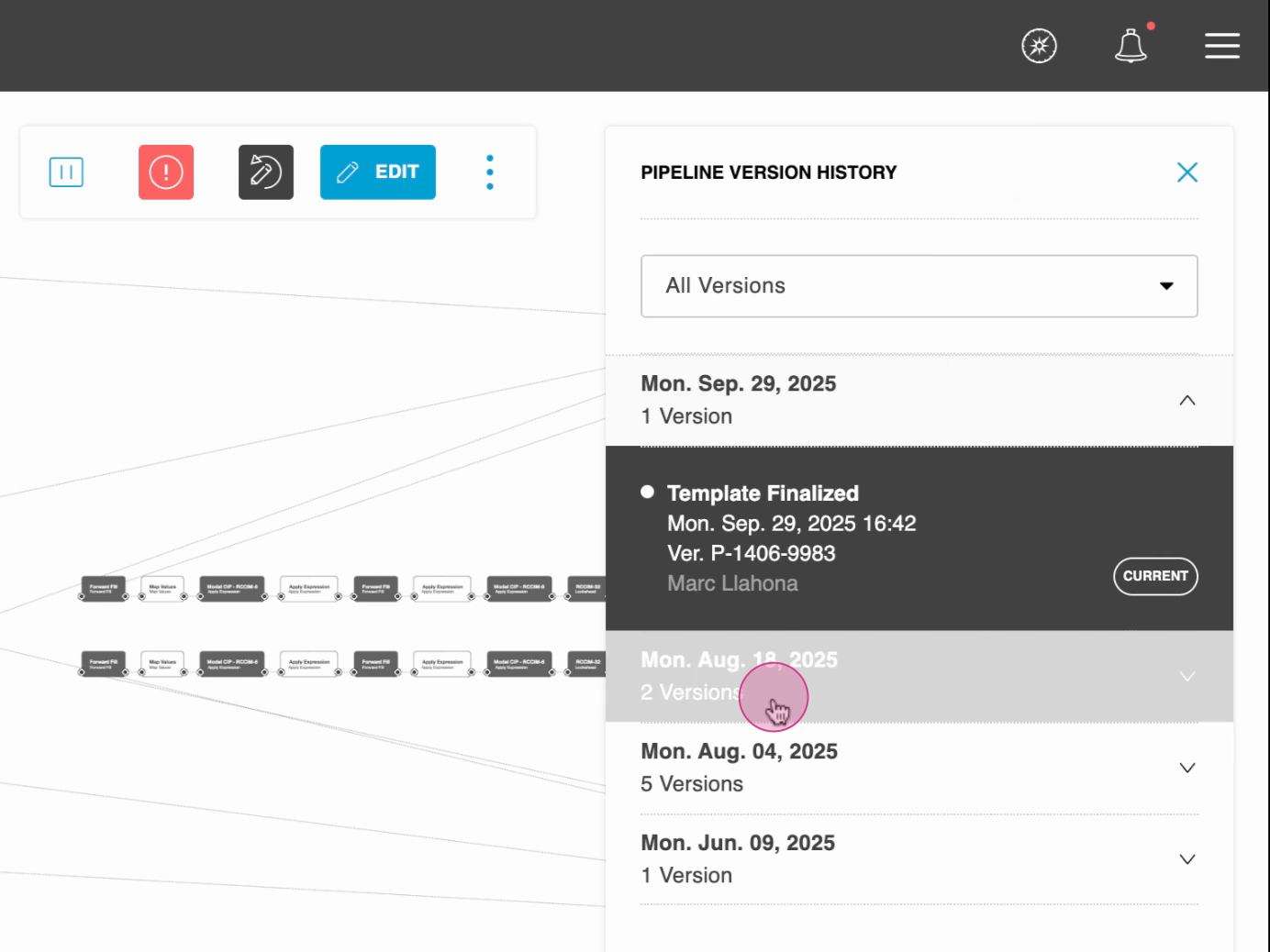
2. Review Versions
When a version loads, two modes are available:
Compare Mode
Highlights differences between the selected version and the current pipeline.
Operator changes:
Green = Will be added if version is restored
Red = Will be removed if version is restored
Yellow = Modified configuration
Provides clarity on what restoring will add/remove.
Exact Version Mode
Displays the pipeline exactly as it existed, including templates and data dictionaries, at that point in time.
You can:
Explore the DAG
Preview data
Inspect operator configurations
3. Restore a Version
Select a version.
Click Restore Version.
Review the confirmation message (lists all changes).
Includes warnings about shared templates and data dictionaries
Impacted pipelines will be transitioned to Edit mode
Confirm restore.
Keep in Mind:
Restoring creates a new version that becomes the current pipeline.
Previous versions remain available — no work is lost.
Best Practices
Use manual saves at major milestones with short, descriptive titles.
Always check Compare Mode before restoring.
Communicate with your team if restoring affects shared templates.
Remember: every restore creates a new version, so nothing is ever lost.